Stop and Frisk Numbers Show Racial Disparities for Downtown Precincts
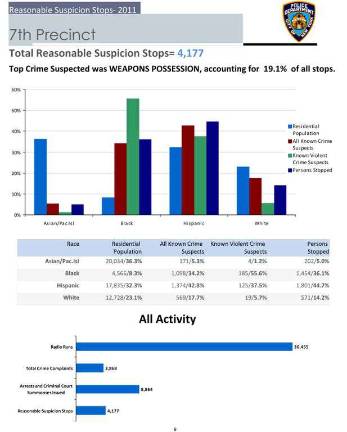
The 2011 NYPD data on the controversial policy bears out common criticism of the practice The NYPD recently re-released citywide Stop and Frisk data from 2011 that reinforce what many opponents of the controversial policy have criticized: Almost 90 percent of all people stopped and frisked citywide in 2011 were minorities. The statistics were re-released just in time for the trial next month that will determine the legality of this police practice. The statistics, which were also divided by precinct, showed that minorities were even more likely to be stopped in neighborhoods with higher percentages of white residents, like the Lower East Side. In the 1st precinct, even though blacks and Latinos only make up 27 percent of the population, they constituted 85 percent of all stops. In the 9th precinct, blacks and Latinos make up almost half of the population, while almost three-quarters of all stop and frisks in 2011 were black and Latinos. "It's not really 'I don't like you because you're black or Latino'; it's 'I see you as a potential criminal,'" said Babe Howell, a professor at CUNY School of Law explaining her theory on the numbers. "If you stop a black or Latino kid, chances are you aren't stopping someone who will be related to the mayor or a city council member." But according to Robert Gangi, the director of PROP, the Police Reform Organization Project, people on the street can only be stopped if they look suspicious, or are committing a crime. In addition, police can also stop an individual if they fit the description of a known criminal in the area. Gangi said that although this practice is legal, sometimes police officers go over the top. "There's a lot of pressure for police to meet their quotas and in a desperate effort to do so, they will engage in unwarranted or illegal stops," said Gangi. NYPD statistics show that not only did stop and frisks increase steadily from over 540,000 in 2008 to almost 686,000 in 2011, but crime has also steadily decreased. Murders are down 43 percent, and this year, on Nov. 26, not a single person was reported stabbed, shot or slashed, according to the NYPD. Nick Viest, the chair of the 19th precinct community council on the Upper East Side said that he supports the NYPD Stop and Frisk policies. "From what I've witnessed, they've handled these things very professionally and appropriately," said Viest. "When you look at these statistics at face value, people get concerned, but they are responding to specific descriptions. They are doing the job necessary to keep the community safe." As far as stopping those who fit a certain description, Victor Goode, a professor at the CUNY School of Law, said that he doesn't quite buy that explanation. "Let's say there a report of purse snatching [by] a young African-American male, 14-16 years old," said Goode. "When the suspect is characterized as broadly as that, it gives them an excuse to stop almost anyone." Next month, Darius Charney, a senior staff attorney at the Center for Constitutional Rights, and his colleagues, will try to challenge the constitutionality of NYPD Stop and Frisk practices like these. However, he did stress that Stop and Frisk is not an illegal police tactic in and of itself. "Their argument that black and Latino people are more likely to commit crimes is not the best, because these are law abiding folks that are being stopped," said Charney. "Are you saying that black and Latinos are more likely to look suspicious?" The trial, "Floyd vs. The City of New York," a class action lawsuit, is set to begin on March 11.